Home > Research > Research Results > Research Results 2017 > Environmental factors that determine the distribution of soil carbon stocks in Japanese forests
Update:July 27, 2017
Main content starts here.
Environmental factors that determine the distribution of soil carbon stocks in Japanese forests
| Article title |
Assessment of soil group, site and climatic effects on soil organic carbon stocks of topsoil in Japanese forests |
|---|---|
| Author (affiliation) |
Kazuki Nanko (a), Syoji Hashimoto (b), Satoru Miura (b), Shigehiro Ishizuka (b), Yoshimi Sakai (c), D. F. Levia (d), Shin Ugawa (e), Tomohiro Nishizono (f), Fumiaki Kitahara (g), Yoko Osone (PD) (b), Shinji Kaneko (h) (a) Department of Disaster Prevention, Meteorology and Hydrology, FFPRI, Tsukuba,Ibaraki, Japan. |
| Publication Journal |
European Journal of Soil Science, 68(4): 547-558, June 2017, DOI: 10.1111/ejss.12444( External link ) |
| Content introduction |
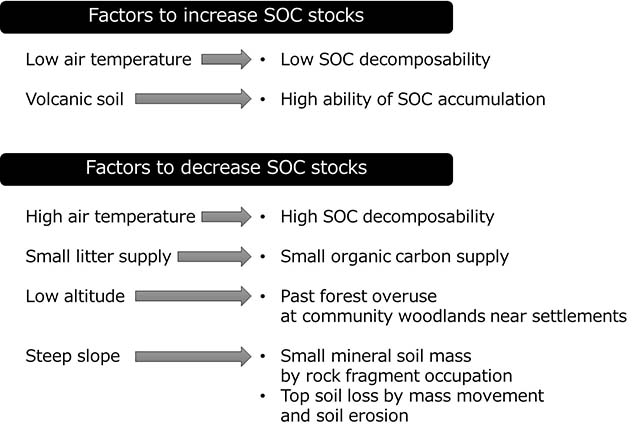
Soil organic carbon (SOC) stocks in forest is a couple of times higher than organic carbon stocks in forest stands. To understand the role of forests in climate change, the accurate estimates of the soil carbon pool are required. Japanese forests distribute on complex topography and various climates zones from subpolar to subtropical. The distribution of SOC stocks in Japanese forest is extremely complex, and the diverse environmental factors that affect SOC stocks remain unclear. Using the latest data-mining techniques to analyze data from the National Forest Soil Carbon Inventory and the National Forest Inventory, we revealed the environmental factors that influence the SOC stocks in Japan. SOC stocks increased with the decrease of air temperatures and in volcanic soil, whereas decreased with the increase of slope inclination and the decrease of litter supply and altitude. The balance among these relationships determined the SOC stocks. These results, based on nationwide survey data, quantitatively showed that the distribution of SOC stocks in Japanese forest was determined by a complex combination of factors comprising soil type, climate, topography, and accessibility to forest as determined by altitude. We clarify the complex processes to determine the distribution of SOC stocks in Japanese forest, derived from the uniqueness and complexity of the Japanese landscape. Our results will improve prediction models of carbon cycle in Japan. Note: Data mining technique: Method of analysis applied to large quantities of data for discovering relationships and patterns hidden within the data., please see another Reserch Results titled: Data mining techniques to improve the accuracy of predicting global soil carbon distribution (http://www.ffpri.go.jp/ffpri/en/research/results/2017/20170428-02.html).
Figure. Factors determining SOC stocks in Japanese forests. |
Copyright © Forest Research and Management Organization. All rights reserved.