Home > Research > Research Results > Research Results 2019 > Three enterprise strategies have been adopted in the Japanese plywood industry where the use of domestic timber is increasing
Update:July 24, 2019
Main content starts here.
Three enterprise strategies have been adopted in the Japanese plywood industry where the use of domestic timber is increasing
| Article title |
Impact of the change in raw material supply on enterprise strategies of the Japanese plywood industry |
|---|---|
| Author (affiliation) |
Seiji Iwanaga (a) Nobuyuki Tsuzuki (a), Hirofumi Kuboyama (a) (a) Department of Forest Policy and Economics, FFPRI, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan. |
| Publication Journal |
Journal of Forest Research (JFR), 23(6):325–335, October 2018 DOI:10.1080/13416979.2018.1534048( External link ) |
| Content introduction |
In Japan, initially, demand for plywood was being met by production from imported logs and the imported plywood. Maintaining demand-and-supply balance owing to the variations in forest resources and forestry policy of the log and plywood exporting countries was an issue. In recent years, however, the use of domestic timber for plywood production has increased and thus the impact from overseas supply is relatively small. In this background, the present study analyzes the response of plywood manufacturers to the changes in raw material supply and clarifies their strategies. As a result, three enterprise strategies have been identified. The first is a differentiation strategy, which includes additional processing for moth-proof, ant-proof, or flame-resistant treatment for specific uses; the use of only domestic timber as raw materials; and adherence to tropical timber in the growing tendency for use of domestic timber. The second is a focus strategy, which includes obtaining the certification of wood processing and distribution processes for environmental considerations and locating plants near the markets. The third is a diversification strategy, which implies producing diversified products and initiating exports in search for new markets. As the local demand for timber is expected to decline owing to a shrinking population among other factors, more companies are likely to adopt diversification strategies, particularly exporting. The research results will help in formulating strategies for the plywood industry as well as domestic timber processing enterprises aiming to expand their domestic timber supply, which will also be useful in formulating policies to advance the timber industry.
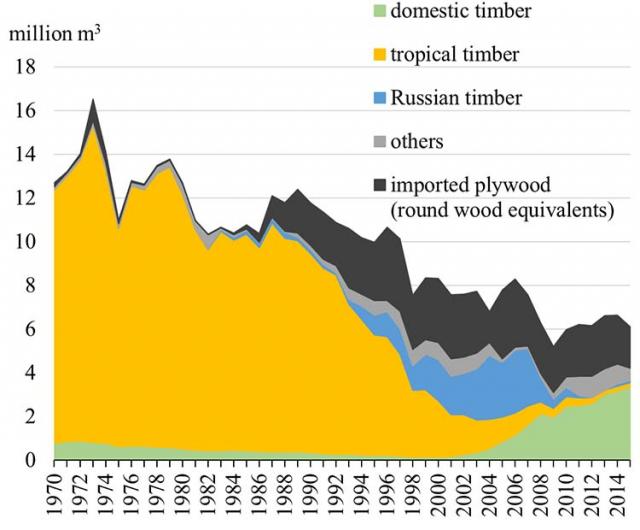
Figure1. Trends of log for plywood use based on originating regions and product imports. Japan’s plywood industry had long relied on tropical timber. Russian timber became popular in the 1990s, thus replacing tropical timber. However, the use of domestic timber increased from the early 2000s onward. As the number of companies using domestic timber grew, product differentiation and diversification strategies were adopted. The data were obtained from the statistical information of Japan Plywood Manufacturers’ Association (2016) and Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan (2016). |
Copyright © Forest Research and Management Organization. All rights reserved.