Home > Research > Research Results > Research Results 2019 > The whole chloroplast genome sequence of Fagus crenata
Update:December 4, 2019
Main content starts here.
The whole chloroplast genome sequence of Fagus crenata
| Article title |
The complete chloroplast genome of Fagus crenata (subgenus Fagus) and comparison with F. engleriana (subgenus Engleriana) |
|---|---|
| Author (affiliation) |
Worth James Raymond Peter (a), Liu Luxian (b), Wei Fu-Jin (c), Tomaru Nobuhiro (d) (a) Department of Forest Molecular Genetics and Biotechnology, FFPRI, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan. (b) Henan University, Kaifeng, China. (c) FFPRI PD, FFPRI, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan. (d) Nagoya University, Nagoya, Aichi, Japan. |
| Publication Journal |
PeerJ 7:e7026 DOI:10.7717/peerj.7026( External link ) |
| Content introduction |
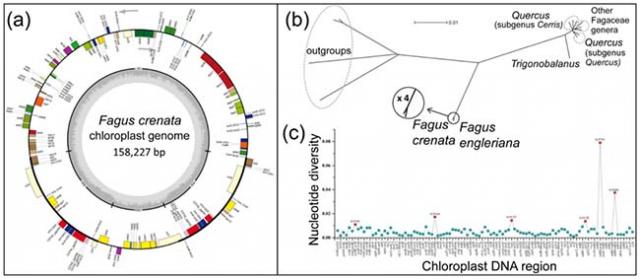
The genus Fagus is an important tree of the northern hemisphere temperate zone (Figure 1). In Japan there are two species, Fagus crenata and F. japonica, which belong to the two different subgenera of the genus, subgenus Fagus and subgenus Engleriana, respectively. Subgenus Engleriana is restricted to East Asia while subgenus Fagus is widespread occurring in East Asia, North America and Europe. In order to investigate the genetic diversity and past processes shaping the distribution of the genus revealing the DNA sequence of seed-dispersed whole chloroplast genome is important. This study reports the whole chloroplast genome DNA sequence of the F. crenata. Overall, the whole chloroplast genome of F. crenata was 158,227 bp in length with 111 genes including 76 protein-coding genes and 31 tRNA genes. The organization of these genes are shown in the whole chloroplast genome map (Figure 2a). Six highly variable regions of the chloroplast were revealed (Figure 2b,c) along with 160 microsatellites (i.e. repetitive parts of the genome that evolve via change in repeat unit number and display high levels of variation that can even distinguish individuals). The whole chloroplast genome of F. crenata, including the identified variable regions, will be an invaluable resource for future research in to the genetic diversity and structure of F. crenata and related species.
Figure 1: An adult tree and nutlet of Fagus crenata. This species is an important part of the temperate forests of Japan.
|
Copyright © Forest Research and Management Organization. All rights reserved.