Home > Research > Research Results > Research Results 2020 > Simple methods for analyzing the development of male sterility in sugi (Cryptomeria japonica)
Update:November 5, 2020
Main content starts here.
Simple methods for analyzing the development of male sterility in sugi (Cryptomeria japonica)
| Article title |
Development of diagnostic PCR and LAMP markers for MALE STERILITY 1 (MS1) in Cryptomeria japonica D. Don |
|---|---|
| Author (affiliation) |
Yoichi Hasegawa (a), Saneyoshi Ueno (a), Fu-Jin Wei (a), Asako Matsumoto (a), Tokuko Ujino-Ihara (a), Kentaro Uchiyama (a), Yoshinari Moriguchi (b), Masahiro Kasahara (c), Takeshi Fujino (c), Shuji Shigenobu (d), Katsushi Yamaguchi (d), Takahiro Bino (d), Tetsuji Hakamata (e) (a) Department of Forest Molecular Genetics and Biotechnology, FFPRI, Tsukuba, Ibaraki, Japan. (b) Niigata University, Niigata, Japan. (c) The University of Tokyo, Kashiwa, Chiba, Japan. (d) National Institute for Basic Biology, Okazaki, Aichi, Japan. (e) Shizuoka Prefectural Research Institute of Agriculture and Forestry, Hamamatsu, Shizuoka, Japan. |
| Publication Journal |
BMC Research Notes 13, September 2020 DOI:10.1186/s13104-020-05296-8( External link ) |
| Content introduction |
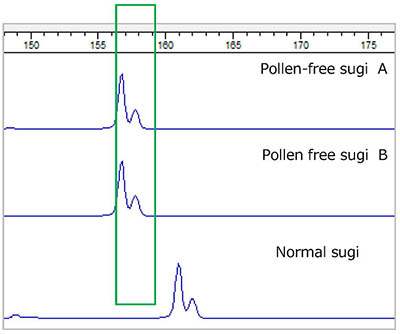
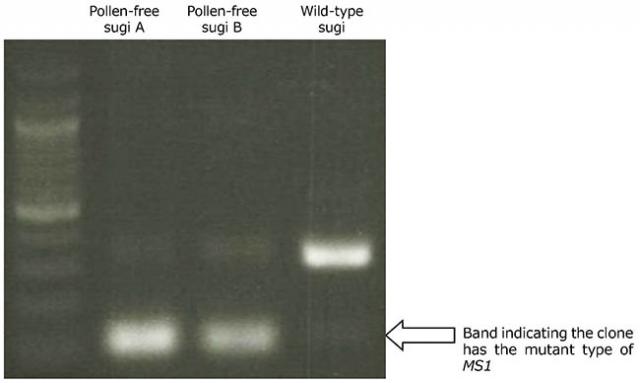
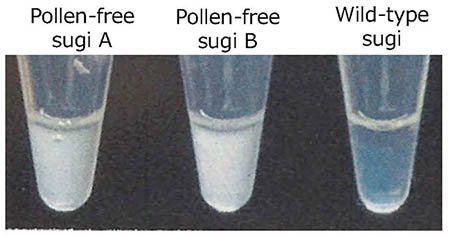
Pollen-free variants of sugi or Japanese conifer (Cryptomeria japonica) are characterized by male sterility, which results in no airborne pollen being produced. To date, four male-sterility genes (MS1–MS4) have been identified in sugi, and approximately 20 pollen-free clones have been selected for MS1 and used to breed a pollen-free cultivar. However, unfortunately, the identification of pollen-free clones requires both the observation of pollen development and artificial crossing, which take a lot of time and effort.To address this, diagnostic genetic markers were developed based on the recently determined DNA sequence of MS1 to allow the type of MS1 gene (wild or mutant) in each individual to be determined. After DNA extraction and subsequent polymerase chain reaction (PCR), the products were analyzed with electrophoresis, allowing the type of MS1 gene to be determined (Photo 1 and Figure 1). In addition, another set of diagnostic markers was developed using the loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method (Photo 2), the results of which led to a patent application named "LAMP primer sets and primer pairs." The application of these methods can reliably detect clones with MS1 mutations.
Photo 1: Detection of pollen-free sugi (Cryptomeria japonica) using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and agarose gel electrophoresis.
Photo 2: Detection of pollen-free sugi (Cryptomeria japonica) using the loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method. |
Copyright © Forest Research and Management Organization. All rights reserved.